Wire Forms: How They Are Made and What They Are Made From
At the most basic level, a wire form is a length of wire that has been formed into a specific shape for a specific purpose. Wire forms come in...
3 min read
![]() Spring Dynamics
:
Nov 18, 2021 7:45:00 AM
Spring Dynamics
:
Nov 18, 2021 7:45:00 AM
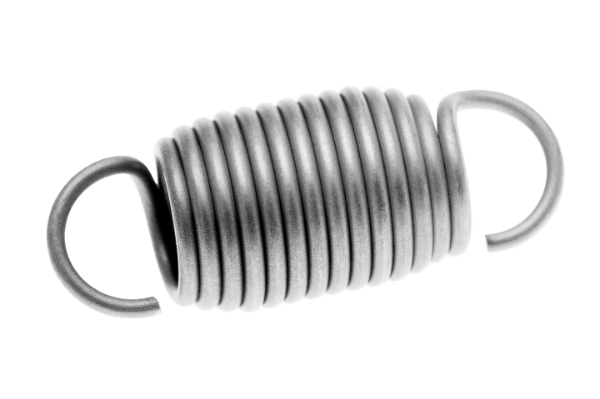
When the average person thinks of springs, they most likely envision an extension spring. Extension springs stretch and get longer, then return to shape. Slinkies are extension springs. So too are screen door mechanisms.
But extension springs are much more than toys or door closers. When used in industry or manufacturing, extension springs come in all shapes and sizes and serve all kinds of purposes.
In this article, we provide an overview of extension springs, their styles, their common uses, and why Spring Dynamics should be your extension spring maker of choice.
Extension springs supply a pulling force. These springs are made from various grades and alloys of round spring steel material. There are various hook configurations that can be applied to extension springs including; Machine hooks, German hooks (arbor cut or extended tabs), English or cross center hooks (as shown below), and side or edge hooks.
Extension springs store energy and exert a pulling force between two mechanisms. When mechanisms separate, the extension spring tries to bring them together again. Extension springs use round wire to create a close-wound design with initial tension.
An extension spring’s ends attach between two mechanisms. The extension springs hooks and loops store and absorbs energy. Through hooks or loops, an extension spring provides return force to connected mechanisms.
More stress in the end hooks—as opposed to the spring body—limits the performance of extension springs.
The most commonly used end styles for extension springs include German-style, machine hook, cross-center, side hook, and double loop ends.
German-style and machine-style ends are the most common end styles. On a German-style hook, the hook radius is extended further from the coil body than the distance of the coil body’s inner radius. The machine-style end has a hook that is raised from half of the coil body so that the inner radius of the hook is equal to the inner radius of the coil body, and the hook radius is as near to the coil body as possible. Both function in the same way mechanically. German-style hooks are slower to produce but yield more consistent hook geometry. Machine hooks are produced in a simpler fashion, therefore have a shorter cycle time, but the trade-off is less consistent hook geometry.
Spring Dynamics manufactures extension springs for a variety of industries and applications. Each spring design is engineered to function in whatever assembly our customer needs. In order to ensure the whole assembly works in harmony, Spring Dynamics works to understand the end-use for each spring and incorporate that knowledge into the customer’s design.
Your product development team is welcome to work with our engineering group to identify which extension spring will work best for your application – in many cases providing advantages not previously considered.
At the most basic level, a wire form is a length of wire that has been formed into a specific shape for a specific purpose. Wire forms come in...

Wire forms are everywhere and are used in nearly every industry and business sector. But what are wire forms and how are they made? In this article,...

When the average person thinks of springs, they most likely envision an extension spring. Extension springs stretch and get longer, then return to...
Are you a manufacturer in need of compression springs for your products? Or maybe just a consumer or entrepreneur looking to learn more about...

Have you ever wondered what keeps a watch running? Or helps a recliner recline? These devices are made possible because of spiral counterbalance...

At the most basic level, a wire form is a length of wire that has been formed into a specific shape for a specific purpose. Wire forms come in...